Augmented Reality Simplified
Augmented Reality Simplified
Rajesh Dangi, May 2021
Augmented Reality (AR) is real, even closer to reality. Using augmented elements layered atop the real-life visuals along with a sound or other sensory stimulus, augmented reality enriches the value of our perceptions, interactions, and overall experience. There are many success stories and use cases of AR that are becoming part of our lives seamlessly transforming the way we learn, interact, and experience the world around us.
As human nature, we love to interact and learn when we use more than one of our sensory capabilities like we taste the food and smell the food, making it an aromatic experience. Similarly, when we learn we read and recite the content to remember, this two-dimensional sensual interaction becomes effective, engaging, and thus easier to remember. The wide adoption of AR is thus not a surprise, across multiple domains ranging from education, manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and eCommerce, etc. have many proof points about leveraging this technology.
In 1968, Ivan Sutherland from Harvard created a head-mounted display system of AR and superimposed virtual simulations on the physical environment paving way for AR adoption for aviation, military, and industrial purposes. From the legacy of not so recent past examples like, Morton Heilig’s Sensorama, Ivan Sutherland’s “Sword of Damocles” VR headset, and Edwin Link’s “Pilot-Maker” flight simulator we have crossed multiple milestones and laid the foundation of many more inventions contributed to the cutting-edge technology called AR, leading the wave of transformation and testimonials that support our vision of reality. Almost after a decade, in 2008 BMW marketing team used AR for visualization of the BMW mini car model via device cameras pointing to the printed media advertisement. This was the path-breaking moment since the users could now experience the look and feel of this car in three dimensions and thus paved the way for augmented reality to the next level of digital experience for the masses.
Today, the augmented reality has become part of our life and we have experiencing it like the trajectory of cricket balls shown on the TV during the live telecasts or the popular ‘Pokeman Go’ mobile game and even in the video conferencing applications filters for AR masks and avatars, and custom backgrounds, etc
Augmented reality and virtual reality are two sides of the same coin, given that each has a different purpose and underlying technologies. The augmented reality makes the best of both worlds as it stimulated the human senses' closure to reality while virtual reality is a computer-generated simulation where one’s environment is replaced artificially. Simply, Augmented reality adds virtual components such as digital images or visuals, vibrations, or sensations (sound and smell) as a new layer of interaction coupled with the actual physical experience.
Over the period from 2017 to 2025, the augmented reality market size is estimated to increase by over 195 billion U.S. dollars, increasing from roughly 3.5 billion in 2017 to over 198 billion U.S. dollars in 2025, mentions Statista
Technology POV - What makes an AR?
Since AR is all about experience, the hardware components and software components are blended together for the effective rendering of AR, the devices could be a smartphone, specialized displays (HUDs), glasses or AR headsets, wearables like VRDs ( Read, Virtual Retinal Display) powered by a strong backend of AI-driven software to integrate the augmentation with real-world via images, coordinates and camera angles/visuals, etc. the algorithms specially used in AR called augogram is a specialized field of study under augography, a science and discipline in itself. Thus, the cameras, sensors, displays, and the applications/algorithms must work in tandem to ‘immerse’ the users with near real experience.
To effectively deliver an AR experience there are three aspects that need to be looked at, an augograph as a combination of real and virtual world images, real-time interaction within the framework, and accurate 3D registration of virtual and real objects. The role of artificial intelligence in augmented reality is fundamental to the core and the complex use cases with multiple technologies interplaying together simply cannot rely solely on human programming to display virtual objects against a real-world backdrop. Neural networks and machine learning can accomplish these tasks with far higher efficiency and can improve augmented reality experiences drastically.
There are several techniques used for feature detection methods like corner, blob or edge detection or thresholding, and few other image processing methods and markers. Markers are visual cues that trigger the display of the virtual information when a distinction is made between two distinct modes of tracking, known as marker and markerless. The Markerless tracking or instant tracking user positions the object in the camera view preferably in a horizontal plane. It uses sensors in mobile devices to accurately detect the real-world environment, such as the locations of walls/objects and points of intersection and angle of interaction, etc. to perfectly vectorize the image coordinates for rendering in the simulated context, known as AR scenes. ARML is a data standard to describe and interact with AR scenes and deals with the location and appearance of virtual objects in the scene and properties of the virtual objects in XML format.
With a large-scale interest in AR application development, the community soon realized the need for software development kits (Read, SDKs) to allow the developers’ community to standardize solutions and shortcuts in development, instead of solving all generic and typical problems grounds up. Today there are multiple SDKs and development frameworks available for building focused use cases for smartphones, wearable glasses, or even plain browser-based AR applications. Vuforia, ARToolkit, ARkit, Wikitude, ARCore, EasyAR, DeepAR to name the few toplines SDKs popular among the developers, most of these are supporting SLAM, 3D object tracking, screen recording and simultaneous detection, and marker-based and marker less location and tracking for multiple types of targets and native platform API’s and provide seamlessly support for Objective C (iOS) and Java (Android), whilst cross-platform support for all major platforms including Mac OS, iOS, Android, Windows, and Unity 3D.
Real-world examples of AR
Apart from Gaming, the leverage augmented reality is providing to industries like automotive, engineering, education, healthcare, retail, real estate & tourism, sports and even military is remarkable, transformational and indeed seen a large-scale adoption.

- In Automotive, let us say for vehicle design with the projectors, car designers overlay appropriate AR images on physical car models and evaluate different design options aiding real-time decision making for prototyping, further helps technicians perform AR aided assembly and maintenance on the shop floor. In the showrooms or online portals, customers can experience the models with a choice of colors, upholstery, and even HUDs the entire user experience is driven by augmented reality. The navigation systems for example are transforming the way users interact and navigate is a game-changer as HUDs are pulling in the real-time GIS information and rendering it to the drivers for safer and effective driving keeping their eyes on the road.
- The Engineering sector is blooming with AR from technical training, model prototypes, computer-aided design (CAD) assembly and maintenance connecting technicians with drawings, simulated process flows, the real-time data from heat sensors and flow meters represented overlapping the industrial equipment are not only providing engaging activities but helping better efficiencies and productivity KPIs. For example, the airline industry is using AR for assisting the engineers in the wiring process during assembly, the work instructions are broken down alongside technical drawings and demonstration videos, instant display of technical artifacts of spares, paths overlapping the real equipment, associated technical consultations and thus they achieve quality control in real-time via the AR enables glasses, etc. The flight simulators too are getting more interesting as they now integrate AR enables HUDs to mimic the visuals of the major airstrips and provide near-real experience and enhance the skill competency, the safety of operations, and situational awareness of the pilots to the next level.
- The Education domain brings in AR for transforming the traditional learning models into interactive, self-paced, and remotely enabled engagements. AR is brought in the elements of interaction and creativity in students to remember and process the content. The interactive participation of students in the learning process not only simplifies the concepts but helps them internalize the experience while they engage in the AR simulated activities so much so that the ‘homework’ becomes a ‘hobby’ and fosters collaboration between teachers and students.
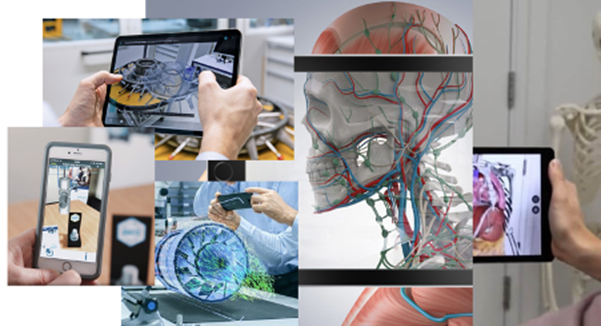
- The major beneficiary of AR is undoubtedly Healthcare since it impacts the livelihood and well-being prominently helping in many areas include vein visualization, surgical visualization, simulation, and education, the life sciences domain also leverages AR to help in creating rich, interactive experiences that show how new drugs and medical devices interact with the body, a surgeon can use constructs of 3D visuals of organs from different angles for greater precision in stitches and trace exact location of veins, etc when drawing blood or starting an IV prior to surgery and even demonstrate the movement of drugs /medicine through the organ and its effects as part of a new treatment or the procedures. The confidence it inculcates when the doctor uses AR to visualize the organs simulates the procedures to patients as part of a consultation explaining diagnostics, a disease state, treatment method particularly as companies are bringing more complex therapies and combination medical devices to patients’ line of treatment, etc. thus significantly enhancing customer engagement and understanding.
- The Retail is buzzing with new products, SKUs and are leaning more and more towards digital engagement with their consumers, just like for apparel company the virtual try-on of different styles offered via AR to their prospects on their own devices from the comfort of their homes ensures traction, engagement and finally conversion. It reimagines the digital shopping experience with virtual storefronts to the consumer. There are many brands that are advertising and collocating within AR games, and digital storefronts and virtual closets where buyers can play, explore, and shop with friends leveraging the digital entertainment approach and benefitting by connecting with new, younger consumers from the vibrant gaming community.
- Finally, it would not be prudent not to mention AR in sports, an entire fraternity of sports enthusiast, coaches, players, and even broadcasters would have benefited from the use of AR in sports, be it the gamification of popular sports, mobile games, marketing, and advertising, merchandising, training and actual telecast that people like on re-plays and trajectories of the balls, stokes and distribution analysis of the batting in cricket, there is so much to talk about AR enriching the level of sports entertainment and fan engagement. The players too are getting benefited with playback of their practice videos and AR overlays on the techniques of their stance, strokes, and swings, etc. This space too is exploring new applications of AR technologies and indeed augmenting them at a greater pace…
In Summary, Augmented reality is augmenting our lives and ‘things’ around us digitally transforming the content and context thereof. From self-driving or connected cars, aircraft simulators, virtual try-on for online stores, remote diagnostics, the AR has and will change the way we experience our world, the way industries design and deliver that experience, and the technologies that enrich the value of that experience. The advancements in emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT, and even 5G will keep the AR space buzzing with new accolades, empowering unification of the physical and digital world for us!