FWaaS, Explained!

FWaaS, Firewall as a service is simply network zoning with firewall partitioning that is virtually isolated and logically grouped policies and rules thereof, each virtual Firewall has multiple such policies tied down to multiple rules (Read, Access control lists, i.e ACLs) thus making it a great proposition as an optimized service running on physically shared devices or cloud instances going completely virtual in a revolutionary way of delivering firewall and other network security capabilities as a cloud subscription service.
In the 2017 Magic Quadrant for Unified Threat Management (SMB Multifunction Firewalls), the analysts reference a Gartner client survey indicating 14% of respondents were likely (8%) or very likely (6%) to consider moving all the firewall security functions to FWaaS. According to Gartner's report, Firewall-as-a-Service is a firewall delivered as a cloud-based service that allows customers to partially or fully move security inspection to a cloud infrastructure.
FWaaS is simple, flexible and more secure, and it results in faster deployment and easier maintenance
FWaaS is in demand, as rapid digitization and data growth, transformation of data-driven business, and ever-increasing threats of cyber-attacks on BFSI, healthcare, and retail industry in developing countries such as India and China, is driving the uptake of security solutions and services thereof. FWaaS takes advantage of advances in software and cloud technologies, to deliver a wide range of network security capabilities on-demand wherever businesses need, including URL filtering, network forensics, and infection prevention.
The key FWaaS offerings are broadly categorized into four tenets based on the features and functionality.
- Proxy Server - A firewall proxy server essentially turns a two-party session into a four-party session, with the middle process emulating the real hosts. Because it operates at the application layer, proxy servers are also referred to as application layer firewalls. Proxy servers are almost always one-way arrangements running from the internal network to the outside network.
- Stateful Inspection Firewall - Stateful inspection, also known as dynamic packet filtering, is a firewall technology that monitors the state of active connections and uses this information to determine which network packets to allow through the firewall. In Stateful inspection firewall analyzes packets down to the application layer. By recording session information such as IP addresses and port numbers, (Read, Sockets) a dynamic packet filter can implement a much tighter security posture than a static packet filter can.
- Unified Threat Management (UTM) - consolidates multiple security and networking functions all on one instance to protect from the risks posed by ransomware, phishing, and other evolving cyber security threats via added integrated endpoint, sandboxing, and other security functions along with additional networking extensions and cloud-based management.
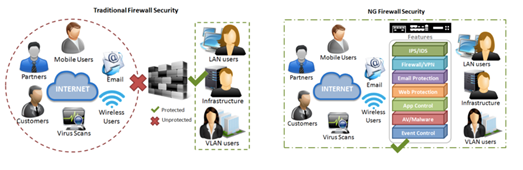
- Next-generation Firewall (NGFW) is a part of the third generation of firewall technology, combining a traditional firewall with other network device filtering functionalities, such as an application firewall using in-line deep packet inspection (DPI), an intrusion prevention system (IPS). Other techniques might also be employed, such as TLS/SSL encrypted traffic inspection, website filtering, QoS/bandwidth management, antivirus inspection and third-party identity management integration (i.e. LDAP, RADIUS, Active Directory). NGFWs offer administrators a deeper awareness of and control over individual applications, along with deeper inspection capabilities by the firewall. Administrators can create very granular "allow/deny" rules for controlling use of websites and applications in the network.
What are the FWaaS Feature Benefits?
- Scalability - FWaaS truly eliminates the appliance form factor thus making it most versatile deployment be in the remote branches or central locations on demand, thus liberates appliance limitations to scale. Since FWaaS is faster to deploy and is very flexible to grow at ease without the need of having to invest in expensive appliance upgrades this means a rapid deployment, seamless upgrade, elasticity and elimination of all the challenges involved in managing appliances on your own.
- Segmentation & Segregation: act or practice of splitting a computer network into subnetworks, each being a network segment, advantages of such splitting are primarily for boosting performance and improving security with visibility and full understanding of internal networks, IPs, VLANs, NAT and routing decisions etc. Segregation is typically achieved by a combination of firewalls and VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks). FWaaS can allow the creation and management of micro-segmented networks in line with defense in depth principle of network security. The reduced congestion improves performance, because on a unified network there are fewer hosts per subnetwork, thus minimizing local traffic. With technologies such as VmWare-NSX, many cloud providers offering VCloud services for micro-segmentation that provide granular controls for east west traffic as well via instance/host level implementation of firewalling, routing and switching highly integrated with the cloud orchestration layer..
- On demand Performance - with flexibility and unrestricted scaling the limitations of physical devices are no longer a constraint, with FWaaS running in the cloud, the performance enhancements are readily available to scale and expand depending on the cloud resources allocated, this helps in sudden surges in the demand due to heavy utilization or simply user base or traffic without compromising on the feature and functionality managing increased load from higher traffic volume or additional processing is required to decrypt an increased volume of SSL traffic etc based on real-time use cases.
- Limited appliance sprawl - FWaaS eases Installation, configuration, policy management, maintenance / upgrades, which otherwise requires efforts and adds complexities to operations.
- Unified security & access policy - FWaaS has ability to uniformly apply the security policy across all traffic, from and for all locations and devices including mobile, remote and fixed users with centralized access management and security policy, enabling network-wide policy definition and enforcement and audits thereof, making it compliance ready. Another major capability FWaaS must deliver is antivirus and anti-malware, zero-day protection such as APT and attempts to classify all traffic, which provides a positive enforcement model (default deny). Solutions with a negative (default allow) model allows all unknown traffic.
- Traffic inspection and remote access: full stateful inspection of both the WAN and internet traffic, SSL inspection and threat prevention capabilities such as UTM, IPS, Filtering and in addition, a FWaaS should allow remote connections from all locations and mobile users integrating with 2FA authentication services as subscribed. It must be capable of decrypting and inspecting that SSL traffic and also be flexible enough to bypass selected segments of SSL traffic via policy.
- User and application awareness & control: the stateful inspection feature also has ability to set and enforce security policies based on the user identity, location and machines while accessing applications or URLs learning from network traffic with deep inspection of packets. The application awareness and control is a differentiator since it understand and responds to same application but with different policy controls depending on the risk profile.
- Pay as you Go - all the feature mentioned about comes with a pay per use pricing model wherein you are charges based on the features you subscribe and resources you decide to host your FWaaS on the cloud, at times you get a bundled price and ability to opt-in and out without any exit barriers or long-term contract obligations.
- Add on Services - FWaaS offering also include and provide for Firewall Management Software/ Tools, Auditing and Compliance, Cloud Security, Connectivity Management, Automation & integration capabilities with surrounding ecosystem such as IAM, PIM/PAM and SIEM service, Backup and Recovery etc
With rapid increases in application usage, data services, and connected devices, service providers are looking at new ways to evolve their networks in order to dynamically address massive growth and align their FWaaS offerings to cost-effectively deliver more differentiated services to their customers.
For Telecom providers, Virtual Network functions (VNFs) and Network functions virtualization (NFV) (that will orchestrate VNFs) and software-defined networking (SDN) all driven by FWaaS like fundamentals are leveraging cloud / edge computing that will transform how they build and scale their telecom networks / services with more flexible, distributed and secure architectures to help rapidly deliver new transformed services, reduced time to market and pursue profitable business models.
In Summary, Firewall as a Service market is segmented on the basis of various parameters and services bundled by Cloud service providers (CSPs), they are reinventing their value proposition to achieve cost savings, network agility, automation along with value proposition to their customers. There are quite a few niche players in this segment and also helps the provide insights and value adds based on AI/AL capabilities tied together for Integrated APM opportunities with FWaaS to enable end to end value transformations via their offerings, the space is interesting and getting consolidated with entry of NFVs, SDNs and vCPE/SD-WANs (operates on WAN-Edge) to join the bandwagon!
***
June 2018. Compilation from various publicly available internet sources, authors views are personal.